Table of Contents
As one of the fastest-growing chronic conditions in Australia, more than 300 new cases are being diagnosed each day for diabetes. Approximately 1.9 million Australians live with diagnosed diabetes and two million have the risk of developing this condition soon according to Diabetes Australia as it has become the seventh most common fatal condition in Australia. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic condition characterised by increased blood glucose (or blood sugar) levels. This surge can be extremely effective on the functioning of the organs. The body struggles to manage the blood sugar levels properly. Issues in insulin production could be the cause of diabetes. It’s important to get the diagnosis done after identifying the symptoms.

Different Types of Diabetes Mellitus
It is important to know and have proper knowledge of diabetes mellitus to know which type of diabetes a person has attacked with to overcome the damage that happened due to this condition on other organs and for the management. Let’s discuss these types in the following,
Type 1 Diabetes: When the body’s immune system mistakenly starts destroying beta cells which produce insulin in the pancreas, stopping the insulin production. For managing Type 1 diabetes insulin therapy is required, usually via injection or having insulin pump for the rest of their lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: One of the most common types, and it’s linked with insulin resistance, in which the body cells stop responding to the insulin effectively. Lifestyle, genes, and weight gain leading to obesity are some of the factors that contribute to its development. There is no age restriction and it can affect people at any age. Oral medication, lifestyle changes and insulin therapy depending on the severity and the health condition are required for managing Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes: This condition is usually developed during pregnancy when the body can’t produce enough insulin to meet the increased requirement, which leads to elevated blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes then leads to problems like preterm birth, excessive build-up of amniotic fluid surrounding the baby (polyhydramnios), and increased birth weight, which might result in further complications such as the baby’s shoulder getting stuck resulting in caesarean delivery.
Factors Which Cause Diabetes Mellitus
There are several factors which are involved in the development of diabetes mellitus such as genetics, lifestyle, or environment. Following are some of the major causes;
⦁ Lifestyle habits, poor diet and obesity where a sedentary lifestyle is adopted can result in the development of Type 2 diabetes.
⦁ Family history and genetics play an important role, in increasing the risk of diabetes
⦁ As individuals age the risk of diabetes increases, and usually males are more prone to get this condition than females.
⦁ Sometimes viral infections trigger type 1 diabetes as a result of an autoimmune response where the immune system fights and destroys the pancreatic insulin-producing beta cells.
⦁ Some women who experience gestational diabetes are at higher risk as well
What are the symptoms of Diabetes?
Symptoms may vary between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Common symptoms of diabetes include:
Experiencing an increase in thirst and appetite, unintentional weight changes, or persistent fatigue could be warning signs. Other symptoms might include blurry vision, frequent urination, slow healing of cuts or wounds, and recurrent infections.
However, it’s crucial to remember that not everyone with diabetes will notice all these symptoms, and some might be subtle. If you have concerns, it’s advisable to consult with your General Practitioner for a proper assessment.
When untreated or poorly managed, diabetes mellitus can lead to severe complications, including:
Health complications may arise, including nerve damage that leads to pain or numbness (neuropathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), and issues with your eyes, such as vision loss (retinopathy). Foot problems, which could escalate to infections and even amputations, are also a risk. Additionally, high blood pressure, skin complications, and a weakened immune system are common concerns. Cardiovascular disease is another serious condition that can develop as well.
Management of Diabetes:
Effective management of diabetes is highly individualised and involves collaboration with a healthcare team to tailor lifestyle modifications and medication plans to each person’s needs. Here are key strategies for managing diabetes:
Working with your Healthcare Practitioner:
Discussing the symptoms of diabetes mellitus with your general practitioner as soon as you see visible symptoms is essential. They will not just diagnose it but also create a personalised management plan that could be adjusted via follow-ups through in-person or telehealth consultations. They can also refer you to a diabetes specialist if required.
Some of the severe symptoms like increased thirst, excessive urination, blurred vision, confusion and high blood sugar readings that too persistently, you should urgently seek medical attention as prolonged symptoms may cause further complications.
Balanced Diet:
Try to develop healthy eating habits and focus on a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins whole grains and other healthy fats. Be careful regarding the diet as it should be enough to regulate your blood sugar levels.
Increased Physical Activity:
Increase the physical activity and engage yourself in some of the regular physical activities including, jogging, swimming, cycling or brisk walking to efficiently control blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
Medication:
Take the proper medication, including insulin or prescribed medications as directed by the healthcare provider. For the prescription refills, you can contact Doctor Help.
Frequent Follow-ups:
Consultation and frequent follow-ups with your GP promptly are significant to monitor the effectiveness of medications and make the required adjustments.
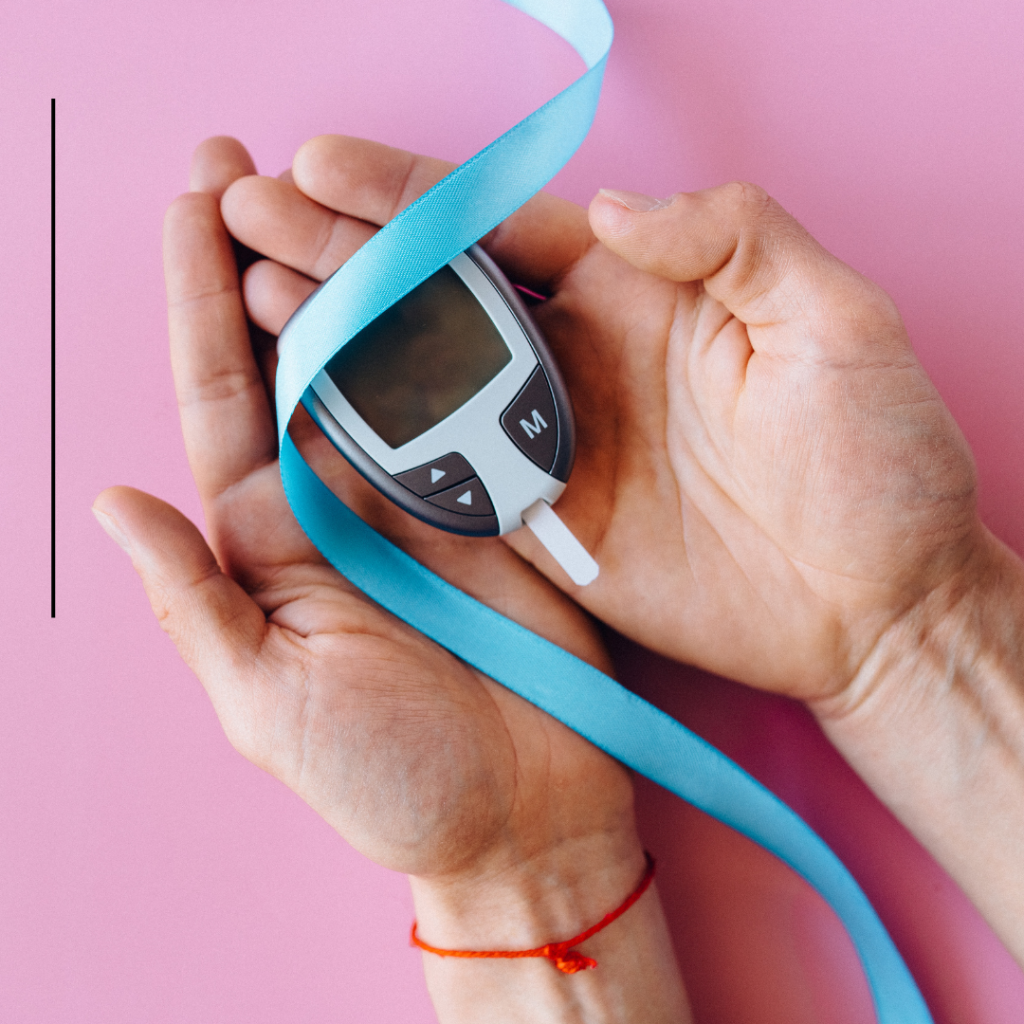
Blood Sugar Monitoring:
As recommended by your healthcare provider make sure to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Stress management:
Sleep and reducing the stress is also important to manage diabetes
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Try to maintain a healthy weight with a combination of physical activity and diet.
Smoking Cessation:
Consider quitting smoking as it can contribute to cardiovascular complications that are associated with diabetes.
It’s important to promptly manage diabetes mellitus through healthy lifestyle changes, checkups, medications and blood sugar monitoring. These are facts that are essential to reduce further complications. Early detection and intervention also play a crucial role in reducing the impact of diabetes on overall health. If you observe any of the above symptoms, make sure to get in contact with the healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.